HHC versus CBD and THC
Let us explore the differences between HHC, CBD, and THC and understand the nuances
In the realm of cannabinoids, HHC, CBD, and THC stand out as notable players, each with its own distinct characteristics and effects. Delving into the intricacies of these compounds sheds light on their unique properties, potential benefits, and differences, allowing consumers to make informed choices.
Estimated reading time: 11 minutes
What is HHC?

HHC, or Hexahydrocannabinol, is a lesser-known cannabinoid that has garnered attention for its psychoactive properties and potential therapeutic effects. While HHC has a structure similar to THC, reports suggest it provides milder euphoria and a more clear-headed experience. Its psychoactive effects likely arise from interacting with the body's endocannabinoid system, though less extensively than THC.
Understanding CBD
CBD, or cannabidiol, has gained widespread recognition for its various potential health benefits, including its purported anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and anxiolytic properties. Unlike THC, CBD is non-intoxicating, meaning it does not produce the euphoric “high” typically associated with cannabis consumption. Instead, it interacts with the endocannabinoid system in a way that promotes balance and homeostasis within the body.
Distinguishing THC
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is perhaps the most well-known cannabinoid, renowned for its psychoactive effects. It is the primary compound responsible for the intoxicating effects of cannabis. THC binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain, resulting in alterations in sensory perception, mood, and cognition. While it has recreational applications, THC also possesses potential therapeutic properties, including pain relief and appetite stimulation.
Key Differences – Psychoactive Effects

HHC
The psychoactive effects of HHC, or Hexahydrocannabinol, are a subject of growing interest within the realm of cannabinoids. Unlike THC, which is renowned for its potent psychoactive properties, HHC is reported to induce a milder euphoria. This distinction makes HHC potentially appealing to individuals seeking a less intense experience while still desiring some level of psychoactivity.
Scientists have not fully understood the exact mechanism through which HHC produces its psychoactive effects. However, they believe it interacts with the body's endocannabinoid system, although to a lesser extent than THC does. This interaction might modulate neurotransmitter release and neuronal activity, altering mood, perception, and cognition.
Users of HHC have described its psychoactive effects as providing a sense of relaxation, euphoria, and heightened sensory perception. Some have reported feeling more clear-headed compared to the foggy-headedness often associated with THC consumption. Additionally, HHC may exhibit a shorter duration of action compared to THC, with users experiencing a relatively rapid onset and offset of its effects.
It's important to note that individual responses to HHC can vary depending on factors such as dosage, tolerance, and personal physiology. While some individuals may find HHC's psychoactive effects enjoyable and manageable, others may experience adverse reactions such as anxiety or paranoia, particularly at higher doses.
HHC offers a unique alternative to THC for individuals seeking a more moderate psychoactive experience. Its milder euphoria and potential clarity of mind make it an intriguing option for those exploring the diverse landscape of cannabinoids.
CBD
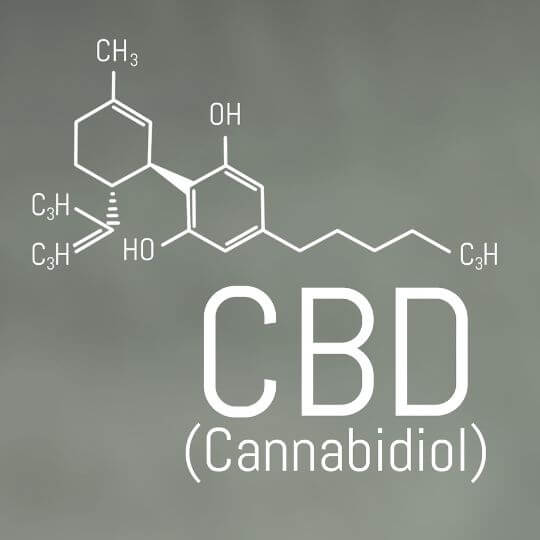
CBD, or cannabidiol, is renowned for its non-psychoactive nature, meaning it does not produce the euphoric “high” typically associated with cannabis consumption. Unlike THC, which binds directly to cannabinoid receptors in the brain, CBD has a more indirect effect on the endocannabinoid system.
While CBD does not exert psychoactive effects in the traditional sense, it interacts with various receptors and neurotransmitter systems in the body, influencing processes such as pain perception, mood regulation, and stress response. By modulating the activity of serotonin receptors, for example, CBD may contribute to its anxiolytic and mood-stabilizing effects.
Studies have shown that CBD may counteract some of the psychoactive effects of THC, such as anxiety and paranoia, by acting as a negative allosteric modulator of CB1 receptors. This means that CBD can bind to CB1 receptors and alter their shape, thereby reducing the binding affinity of THC and mitigating its psychoactive effects.
Furthermore, CBD's ability to enhance the levels of endocannabinoids like anandamide, often referred to as the “bliss molecule,” may contribute to its mood-enhancing properties without inducing intoxication. Additionally, CBD has been investigated for its potential to alleviate symptoms of various mental health conditions, including anxiety disorders, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder.
In summary, CBD's psychoactive effects are characterised by its non-intoxicating nature and its ability to modulate various neurotransmitter systems within the body. While it does not produce the euphoria associated with THC, CBD offers potential therapeutic benefits for a range of conditions without impairing cognitive function.
THC

THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary psychoactive compound found in cannabis. Its psychoactive effects stem from its ability to bind to cannabinoid receptors in the brain, particularly CB1 receptors, leading to alterations in sensory perception, mood, and cognition.
When THC binds to CB1 receptors, it activates the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. This surge in dopamine levels contributes to the euphoric “high” experienced by THC users. Additionally, THC's interaction with cannabinoid receptors influences other neurotransmitter systems, including those involved in memory, motor coordination, and appetite regulation.
The psychoactive effects of THC can vary depending on factors such as dosage, route of administration, and individual sensitivity. Users commonly report feelings of relaxation, euphoria, altered perception of time, and heightened sensory experiences. However, THC can also induce adverse effects, such as anxiety, paranoia, and impaired cognitive function, particularly at higher doses or in individuals predisposed to psychiatric conditions.
Moreover, THC's psychoactive effects can have implications for tasks requiring cognitive and motor skills, such as driving or operating heavy machinery. Impairments in memory, attention, and coordination may pose risks to individuals using THC-containing products, necessitating caution and responsible consumption.
So, THC's psychoactive effects are characterised by its ability to bind to cannabinoid receptors in the brain. Leading to alterations in mood, perception, and cognition. While THC can induce euphoria and relaxation, it may also produce adverse effects and impair cognitive function. Highlighting the importance of informed and mindful use.
Legal Status HHC, CBD and THC
The legal status of HHC, CBD, and THC varies. Depending on the jurisdiction and specific regulations governing cannabis and its derivatives.

CBD, or cannabidiol, is legal in many regions. Provided it is derived from hemp plants containing less than 0.2% THC. In the UK, CBD products are widely available and can be legally sold as long as they meet certain criteria. It must be derived from EU-approved hemp strains and containing negligible levels of THC. However, regulations regarding CBD products may vary between countries, and consumers should be aware of local laws and restrictions.
THC, on the other hand, is subject to stricter regulations due to its psychoactive properties. In the UK, THC is classified as a controlled substance under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971. Furthermore its possession, cultivation, and distribution are illegal without proper authorization. Medicinal cannabis products containing THC are available in limited circumstances. Mostly under prescription from a qualified healthcare professional, but recreational use remains prohibited.
As for HHC, its legal status is less clear-cut due to its relative novelty and limited research. HHC is a synthetic cannabinoid that shares structural similarities with THC, raising questions about its classification and regulation. In many jurisdictions, analogues of controlled substances like THC may fall under similar legal restrictions, especially if they are deemed to have psychoactive properties. Therefore, the legality of HHC may vary depending on how it is classified and regulated within each jurisdiction.
CBD is generally legal in many regions. THC is subject to strict regulations, and its possession and use are often restricted to medicinal purposes. The legal status of HHC is less defined and may depend on specific regulations governing synthetic cannabinoids and analogues of controlled substances.
More from our blogs
Therapeutic Potential of HHC, CBD and THC
The therapeutic potential of HHC, CBD, and THC encompasses a wide range of health conditions and symptoms. Each cannabinoid offering unique benefits and applications.
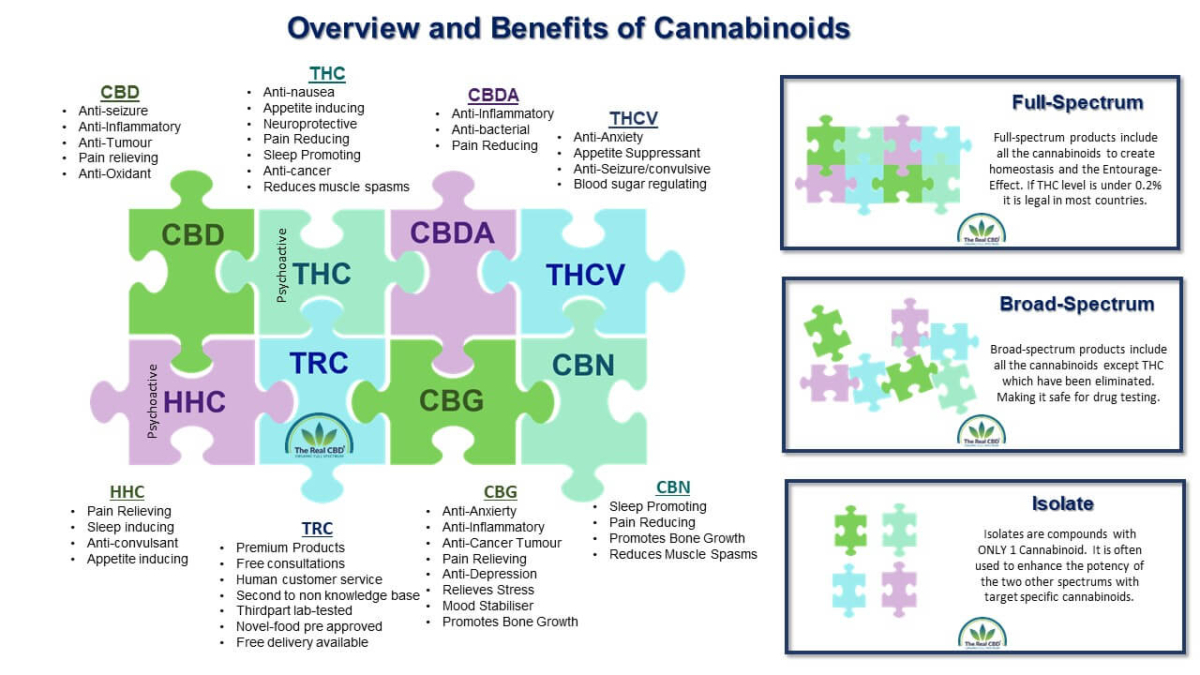
HHC
Starting with HHC, this lesser-known cannabinoid has shown promise in preliminary studies for its potential therapeutic effects. While research on HHC is still limited compared to CBD and THC, anecdotal reports suggest that it may possess analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and anxiolytic properties. Some users have reported using HHC for pain relief, anxiety management, and relaxation. However further research is needed to fully understand its efficacy and safety profile.
CBD

CBD, on the other hand, has been extensively studied for its diverse therapeutic potential. Research suggests that CBD may offer relief from various conditions, including chronic pain, inflammation, epilepsy, anxiety disorders, and insomnia. CBD interacts with the body's endocannabinoid system, as well as other neurotransmitter systems, to exert its effects. Unlike THC, CBD does not produce psychoactive effects, making it a popular choice for individuals seeking natural remedies without the intoxicating effects of cannabis.
THC
It is primarily known for its psychoactive properties, also possesses therapeutic potential. Tetrahydrocannabinol has been studied for its analgesic, antiemetic, appetite-stimulating, and neuroprotective properties. Medicinal cannabis products containing THC have been prescribed for many conditions. Such as chronic pain, chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, and muscle spasticity in conditions like multiple sclerosis. However, the psychoactive effects of THC can be a limiting factor for some people. Particularly those sensitive to its intoxicating effects.
HHC, CBD, and THC each offer distinct therapeutic potential. All with varying degrees of scientific evidence supporting their efficacy for different health conditions. CBD is widely recognised for its therapeutic versatility and non-intoxicating nature. THC may be beneficial for specific conditions but comes with psychoactive effects. HHC, although less researched, shows promise as a potential therapeutic agent, but further studies are needed to validate its benefits and safety profile.
Conclusion
In summary, HHC, CBD, and THC represent distinct compounds within the realm of cannabinoids. Each with its own unique properties and potential benefits. Understanding the differences between these cannabinoids empowers consumers to make informed decisions regarding their use. Whether for recreational enjoyment or therapeutic purposes.
FAQ – HHC vs. CBD and THC

HHC, or Hexahydrocannabinol, is a lesser-known cannabinoid with mild psychoactive properties and potential therapeutic effects. Similar to THC but with a clearer-headed experience.
CBD, or cannabidiol, is non-intoxicating and offers various potential health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and anxiolytic properties. THC is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, responsible for the euphoric “high.”
HHC induces a milder euphoria compared to THC, making it potentially appealing for those seeking a less intense experience. It interacts with the endocannabinoid system, though to a lesser extent than THC.
CBD is generally legal in many regions. THC is subject to strict regulations and is illegal for recreational use in the UK. HHC's legal status is less defined and may vary depending on jurisdiction and regulations.
HHC, CBD, and THC each offer distinct therapeutic potential. CBD is known for its versatility and non-intoxicating nature. THC may be beneficial for specific conditions but comes with psychoactive effects. HHC shows promise but requires further research for validation.
The Real CBD Best Sellers
-
 CBD Capsules – Water Soluble 5%€59.00
CBD Capsules – Water Soluble 5%€59.00 -
 15% Pure CBD oil€80.00 – €85.00
15% Pure CBD oil€80.00 – €85.00 -
 10% CBD oil€55.00
10% CBD oil€55.00 -
 5% Pure CBD oil€29.00 – €35.00
5% Pure CBD oil€29.00 – €35.00 -
 Athlete MCT/CBD oil 18%€90.00
Athlete MCT/CBD oil 18%€90.00 -
 25% Pure CBD oil€139.00
25% Pure CBD oil€139.00 -
 40% Raw CBD Oil€189.00
40% Raw CBD Oil€189.00 -
 CBG/CBD oil€87.00
CBG/CBD oil€87.00 -
 CBD Sleep Solution 10%€50.00
CBD Sleep Solution 10%€50.00 -
 5% CBD oil for Pets€29.00
5% CBD oil for Pets€29.00 -
 2.5% CBD oil for Pets€15.00
2.5% CBD oil for Pets€15.00 -
 10% CBD oil for Pets€55.00
10% CBD oil for Pets€55.00

I am a certified expert in Medicinal Cannabis. We are all about giving correct and trustworthy information. We know how important it is to learn about CBD and cannabis, which is why we want to be your go-to source for trustworthy information. We help you improve your health by using our knowledge and experience as a starting point.














Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!