CBD for the Endocannabinoid System
Home: CBD for the Endocannabinoid System
Estimated reading time: 11 minutes
Table of Contents
- Endocannabinoid System
- The Runners High and CBD
- CBD, Sports, Physiology and Bioenergetics
- Our Appetite and CBD
- Cannabidiol for the Gut Microbiome
- Our Health and the microbiome
- CBD for Digestive Health
- CBD Research
- What is the Epithelial Barrier?
- Findings from the study
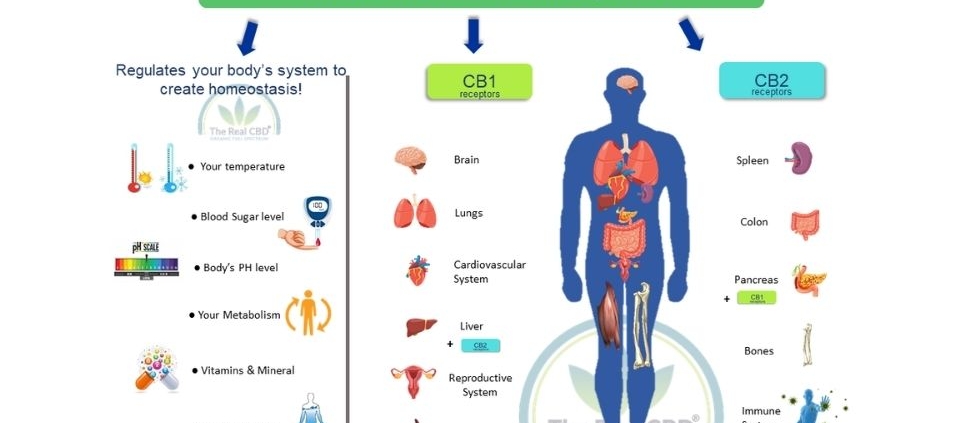
Endocannabinoid System
Scientists discovered in the early 2000s that circulating endocannabinoid levels in the human body increased during exercise. The term “runner's high” took on a new meaning. According to a 2004 article in Runner's World, experts were already questioning the old endorphin model. Turning to cannabinoids, specifically, anandamide binds to the CB1 receptor and produces both pain-killing and euphoric effects.
But the situation was far from resolved. The study of the source and the precise role of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) lasted well into the 2010s. The basic effects of endocannabinoid production during exercise are now widely accepted. Deeper aspects of this connection are still being looked at. Including the legality of cannabis use for athletic performance; the relationships between THC intake and exercise, and other aspects of ECS function. After all, exercise affects systems throughout the body, including heart and breath rates, metabolism, and mental health.
Let's take a look at how CBD for the Endocannabinoid system can be affected by exercise.
The Runners High and CBD

Just a few months ago, The Neuroscientist, a journal aimed at doctors and nurses, published a review with a testy title. “Do Endocannabinoids Cause the Runner's High?” – Evidence and Unanswered Questions. Exercise increases the endocannabinoids in the body. These appear to be linked with feelings of a runner's high, namely lower levels of anxiety and a feeling of high. Also proving less pain following exercise.
The article concludes with a recipe to stimulate endocannabinoid release in the laboratory. According to the study, running is the best way to increase endocannabinoid levels in the blood. Followed by cycling, and the duration should be at least 20 minutes.The authors also note that 30 to 35 minutes of exercise produces the greatest positive mood effects.
What's more..
In addition to showing these broad trends, the analysis revealed some inconsistencies. There were significant differences in the magnitude of the effect across studies. This relates to exercise intensity, physical fitness, the timing of measurement, and/or fasted state. The effects of chronic or long-term exercise on circulating endocannabinoids were also inconsistent. Showing that temporarily elevated levels during exercise are linked with the fleeting “runner's high.”
Read more about CBD and Exercise
CBD, Sports, Physiology and Bioenergetics

CBD may not have a direct impact on the runner's high, but it is not to be overlooked in its potential to enhance physical activity. With its indirect interactions with both CB1 and CB2 receptors, as well as activity at a variety of other receptors, CBD has been known to provide a range of physiological benefits, including pain and inflammation relief, and stress reduction.
In fact, recent research published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences highlights the connection between the endocannabinoid system (ECS) and the metabolic health benefits of exercise. The researchers point out that dysregulation of the ECS can lead to insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and other metabolic imbalances, all of which can be corrected through regular exercise.
While much of this research is still in its early stages, the potential for customized exercise regimens to treat and prevent these dangerous conditions is a promising area for further investigation. So, while CBD may not directly impact the runner's high, it certainly has a role to play in improving overall physical health and well-being.
Our Appetite and CBD
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) regulates our appetite, satiety, and weight when it is functioning properly. CB1 cannabinoid receptors in our brain are in charge of signaling that it's time to eat when we're hungry. Rousing our appetite, and sharpening our sense of smell so food tastes even better. CB2 cannabinoid receptor activation, on the other hand, works to decrease food intake and prevent body fat accumulation.
When only fresh meat, fruits, and vegetables were available to eat, it was easier to keep our ECS in balance naturally. However, our modern diet is so out of whack that our CB1 receptors are stuck in overdrive mode. Reinforcing an abnormal feed-reward-feed loop from all of the sugary, high-fat foods we consume.
When mice were fed a high-fat, high-sugar diet for 60 days, their CB1 receptors became overactive. Preventing the secretion of amino acids that are supposed to reduce appetite when the system is working properly. Our CB2 receptors, on the other hand, are activated by plant-based foods such as leafy and bitter greens, olive oil, and various spices. They are essentially undernourished in a typical Western diet high in carbs and processed food.
Your gut has its own “brain,” which communicates with the brain between your ears.
Deficits in omega-3 fatty acids also alter how our cannabinoid receptors function. These beneficial fatty acids keep our ECS running smoothly. However, if you are deficient in omega-3 fatty acids (as many Americans are), your ECS function suffers.
More from our blog
Cannabidiol for the Gut Microbiome
Your gut microbiome does more than just aid in digestion. It's linked to your overall well-being, including your moods and emotions, through the gut-brain axis. This is a critical connection that medical scientists are paying increasing attention to because it influences inflammation, digestion, and even your mental health. The endocannabinoid system (ECS) plays a key role in regulating the gut-brain axis, allowing for communication between the brain and microbiome. This means that if your diet is negatively affecting your microbiome, it can also impact your ECS and brain function.
Regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining a healthy ECS. Exercise releases natural endocannabinoids that help regulate stress levels and maintain a healthy weight. Unfortunately, many of us spend most of our time sitting, whether at a desk, in a car, or on a couch, leading to a sedentary lifestyle that can negatively impact our health.
The microbiome is a vast community of microorganisms that live both inside and on our bodies. It's estimated to contain the same number of cells as the human body and encodes 100 times more genetic material than the human genome. The gut alone contains up to 1,000 different species of bacteria. With this understanding, it's clear that the health of our microbiome is crucial to our overall health and well-being.
Our health and the Microbiome
As research on the human microbiome continues to advance, it's become increasingly clear that it plays a vital role in overall health and well-being. This complex ecosystem of microorganisms, which resides in the gut, has been linked to a range of health issues including obesity, cancer, and neurological diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's. While much is still unknown about the workings of the microbiome, one crucial factor that has been largely overlooked is the role of the endocannabinoid system (ECS).
Despite the widespread attention given to the microbiome in popular media, the relationship between the ECS and the microbiome has received little coverage outside of scientific circles. The ECS is a complex system of receptors and signaling molecules that helps to regulate a range of physiological processes, including appetite, mood, and inflammation. Research has shown that the ECS also plays a role in modulating the activity of the microbiome, which in turn has implications for overall health and well-being.
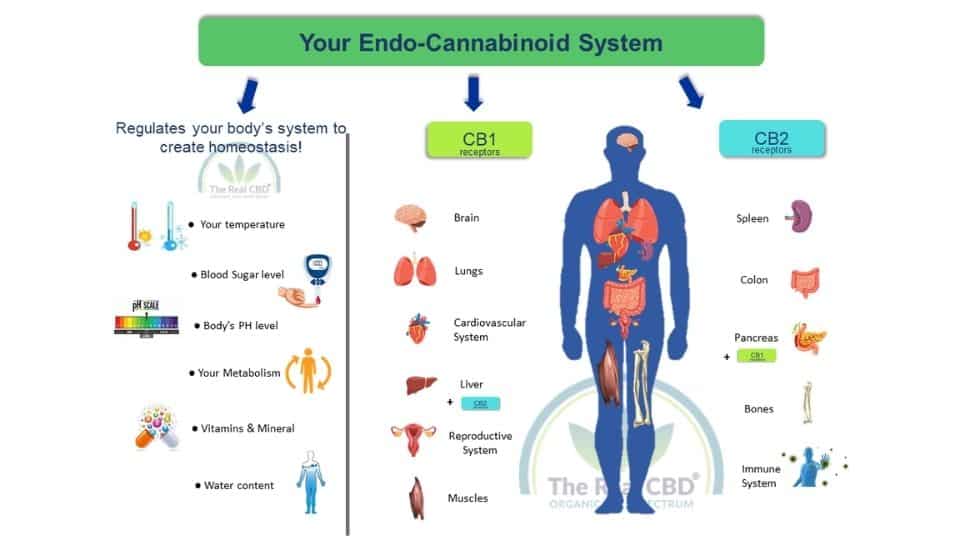
As we continue to unravel the complex interplay between the microbiome and the ECS, it's becoming increasingly clear that this relationship has important implications for human health. By better understanding the role of the ECS in shaping the microbiome, we may be able to develop new treatments and interventions for a range of health issues, from obesity to neurological diseases.
The Role of The Endocannabinoid System
The ECS, according to current thinking, acts as a sort of bridge between bacteria and the body. Here we can include the brain, sending signals back and forth in a symbiotic, mutually beneficial relationship. At least, that is how it should be. But chronic imbalance or impairment of the gut microbiome can be harmful to both physical and mental health.
Humans and other animals influence the “bugs” in their gut mainly through diet. Including the intake of so-called probiotic foods that promote a healthy microbiome. These bugs, in turn, aid in the breakdown of food and the availability of nutrients to the body. We give them food and a comfortable place to live. They then help us extract as much nutrition as possible from food in the digestive tract.
This is incredible in and of itself. However, it turns out to not be enough. Breakthrough research has revealed that we can influence our gut microbiome not only through exercise and certain medicines.
Can CBD improve gut health? – all you need to know!
CBD for Digestive Health

The interactions of gut microbiota and the endocannabinoid system were first investigated in 2010. A Belgian research team discovered altering the gut microbiome of obese mice with prebiotics. Including foods that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria. This altered ECS expression in fat tissue, potentially affecting lipid metabolism and fat cell formation.
The ECS acts as a link between bacteria and the human body. Including the brain, relaying signals in a symbiotic, mutually beneficial relationship.
CBD Research
The bacteria in our gut have a vital role to play beyond just breaking down food. They also play a crucial role in regulating the epithelial barrier, which is a protective layer that lines the gastrointestinal tract.
The composition of our microbiome is determined by a variety of factors, not just our diet, and these microorganisms help to maintain the integrity of the gut barrier. But how exactly do they achieve this important function?
Endocannabinoide system for Pets
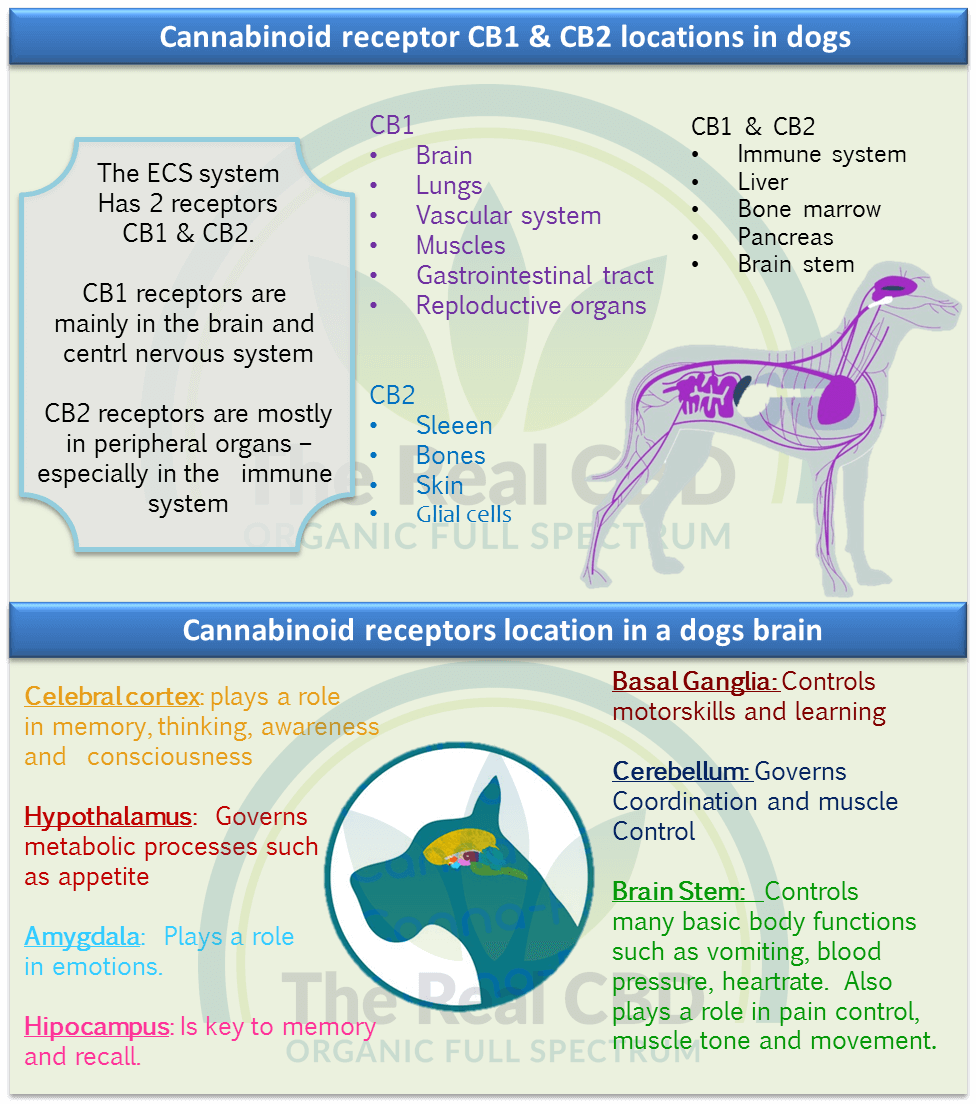
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a very interesting part of our pet friends' complex bodies. This system, which is found in all mammals, is very important for keeping balance and boosting general health. Let's go on an adventure to figure out how the endocannabinoid system in pets works. Gaining a better understanding of its inner workings.
The endocannabinoid system is made up of three main parts: enzymes, endocannabinoids, and receptors. These parts work together to make the body's biological reactions sound like a symphony. The receptors are called cannabinoid receptors type 1 (CB1) and type 2 (CB2). They are found in many different organs and tissues. The way our pets work is intricately woven into their bodies.
Endocannabinoids, which are made by the body naturally, act as signals in this system. They connect to the cannabis receptors like puzzle pieces that fit together well. With this complicated dance, a flood of information is sent out. They set off a number of bodily processes that help keep the body in balance and make it work properly.
Read more about CBD for pets here
What is the Epithelial Barrier?
According to Keith Sharkey, a University of Calgary professor and researcher who has studied the gut for decades. More recently he has shown that the microbiome, the ECS, and the epithelial barrier play a huge role in maintaining overall health and warding off disease. He was also a senior author of the aforementioned 2015 study in which THC was given to mice.
The epithelial barrier is critical for homeostasis, or normal body functions. The body manages the control of that fine lining with great care. As mammals, we have evolved a complex control system that prevents or quickly repairs damage. In order to prevent further aging of our bodies. That system is aided by the bacteria in our gut. And it appears that the ECS is a critical control element.
Findings from the study
Everything points in the same direction. If the ECS communicates with both the gut barrier and the microbiome, both of which are critical to human health. We also know that we can influence the ECS with diet, exercise, and cannabis products. There could be other ways to target the microbiome via the ECS to achieve specific health outcomes.
Breakthrough research has shown that we CAN influence our gut microbiome. Not only through diet, exercise, and certain pharmaceuticals but also through CBD consumption, all via the ECS.
Is it possible that the gut microbiome will alter those cannabinoids, making them more or less active?
-
 40% Raw CBD Oil€189.00
40% Raw CBD Oil€189.00 -
 5% CBD oil with turmeric and black pepper€29.00
5% CBD oil with turmeric and black pepper€29.00 -
 25% Pure CBD oil€139.00
25% Pure CBD oil€139.00 -
 10% CBD oil€55.00
10% CBD oil€55.00 -
 15% Pure CBD oil€80.00 – €85.00
15% Pure CBD oil€80.00 – €85.00

I am a certified expert in Medicinal Cannabis. We are all about giving correct and trustworthy information. We know how important it is to learn about CBD and cannabis, which is why we want to be your go-to source for trustworthy information. We help you improve your health by using our knowledge and experience as a starting point.










Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!