Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
- What are cannabinoids?
- What is CBD (cannabidiol)?
- What is CBDa (Acid form of Cannabidiol)?
- How do cannabinoids interact in the body?
- What is CBN (Cannabinol)?
- What is THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol)?
- What is THCV (Tetrahydrocannabivarin)?
- What is CBG (Cannabigerol)?
- What are Endocannabinoids?
- What is the endocannabinoid system?
- Cannabinoids
- FAQ – Cannabinoids
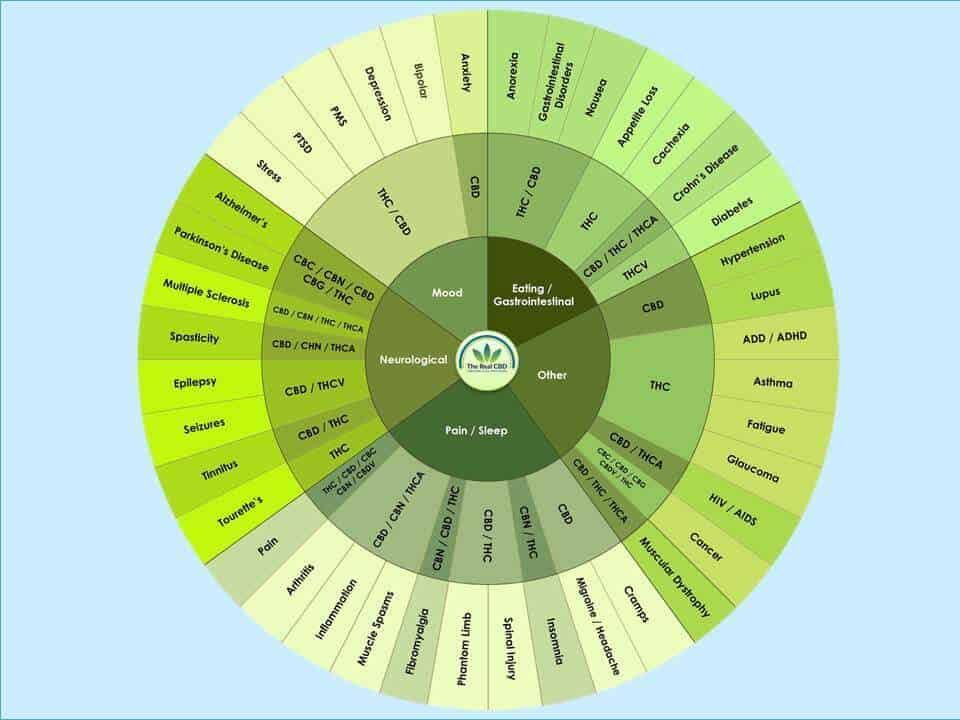
What are cannabinoids?
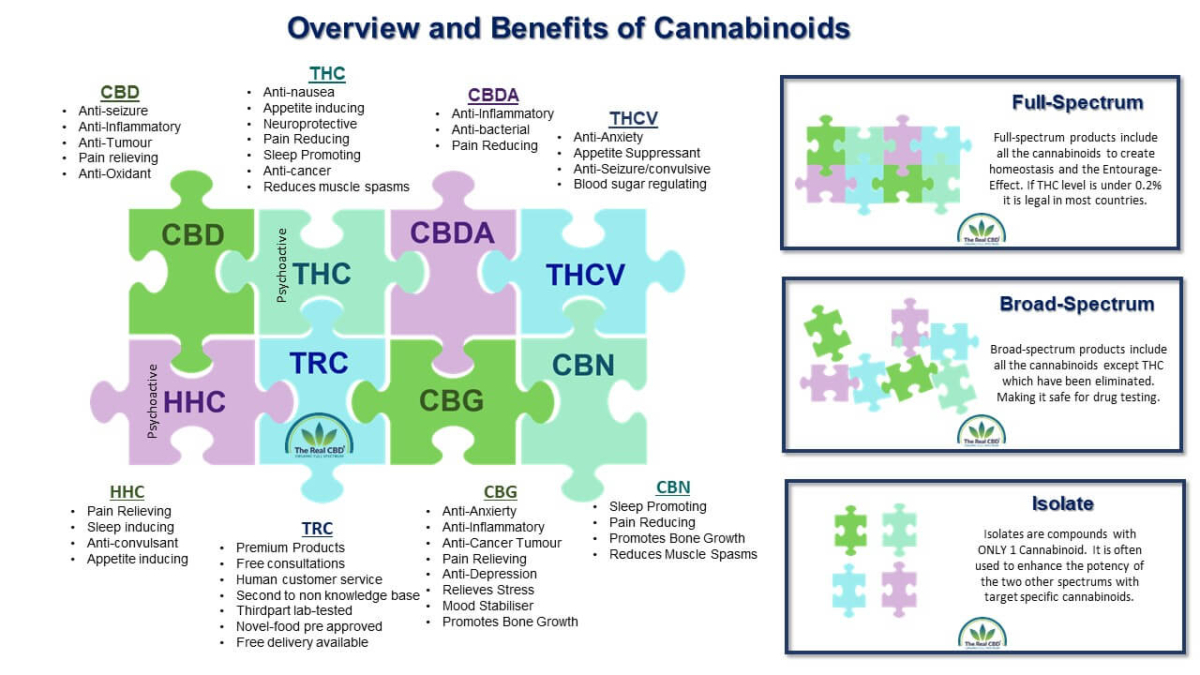
Cannabinoids are a group of natural plant compounds found in the cannabis plant. The most well-known cannabinoids are THC and CBD, but there are many others, including cannabinol CBN, CBG, and CBC.
Cannabinoids works with the body’s endocannabinoid system, a complex cell-signalling system that plays a role in regulating a range of processes in the body, including pain sensation, mood, appetite, and the immune system. The body contains two main receptors of the endocannabinoid system, CB1 and CB2.
The two most famous cannabinoids
THC is the main compound in cannabis that makes you feel “high” when you use it. It binds to CB1 receptors in the brain, which can change perception, mood, and thinking, among other things. THC can also be used to treat health problems. For example, it can relieve pain, stop inflammation, and stop nausea and vomiting.
CBD, on the other hand, does not make you feel high and does not bind to CB1 receptors. Instead, it seems to change how other cannabinoids work and how they interact with many different receptors in the body.
Cannabinoids have the potential to help people, but there are also risks and side effects that could happen if you use them. These can include problems with thinking, a faster heart rate, and feelings of anxiety or paranoia, among other things.
What is CBD (cannabidiol)?
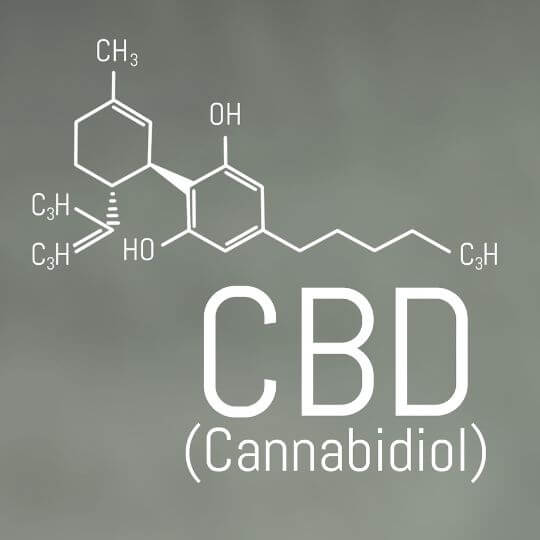
The cannabis plant contains the cannabinoid CBD (cannabidiol) along with other cannabinoids like THC and CBG. Cannabidiol is non-psychoactive, meaning it does not produce the “high” often seen with THC.
This has been studied for its potential medicinal effects. It appears to have anti-inflammatory effects, making it a potential treatment for conditions like arthritis. Additionally, CBD may help reduce pain. CBD has also been studied for its potential as an anxiety-reducing agent, with some studies suggesting it may be effective in treating conditions like social anxiety disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
CBD is used to treat epilepsy. For example, the FDA has legalized a drug called Epidiolex, which contains CBD. To treat two rare forms of childhood epilepsy. CBD may also help protect the brain from diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
What is CBDa (Acid form of Cannabidiol)?
The cannabis plant contains the cannabinoid CBDA. This acidic compound precedes CBD and often appears in higher amounts in raw, unprocessed cannabis plants. Very bitter in taste.
It is non-psychoactive, meaning it does not produce the “high” seen with THC. While CBDA has not been studied as CBD, it appears to have some potential effects. CBDA has been studied for its potential as an anti-inflammatory helper.
Additionally, CBDA may have the potential as helping with nausea and vomiting. Some studies have suggested that CBDA may be effective in reducing nausea and vomiting caused by chemotherapy or motion sickness.
How do cannabinoids interact in the body?

Cannabinoids work with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which is a complex cell-signaling system that helps control things like how we feel pain, our mood, our appetite, and how our immune system works.
The endocannabinoid system mainly consists of CB1 and CB2 receptors. These receptors exist throughout the body. Most CB1 receptors are in the brain and central nervous system. Most CB2 receptors are in immune cells and tissues outside the brain and central nervous system.
Cannabinoids like THC and CBD work with these receptors. This changes how these messages are released, which has a wide range of effects. When THC binds to CB1 receptors in the brain, it can change the way a person sees, feels, and thinks. CBD. On the other hand, seems to change how other cannabinoids work and interact with a lot of other body receptors.
Cannabinoids have other effects on the body that aren’t caused by how they interact with receptors. Some cannabinoids, for example, may change the way enzymes work that help break down dopamine and serotonin.
What is CBN (Cannabinol)?

The cannabis plant contains the cannabinoid CBN, along with other cannabinoids like THC and CBD. CBN forms when THC breaks down due to oxidation, heat, or light. This means that aged or poorly stored cannabis may contain higher levels of CBN.
CBN is non-psychoactive, meaning it does not produce the “high” associated with THC. However, it does appear to have some therapeutic effects. CBN has been studied for its potential as a sleep aid, as it may have sedative effects. Additionally, CBN may have anti-inflammatory effects, making it a potential treatment for conditions like arthritis. Some studies have also suggested that CBN may have antibacterial properties.
More from our blog:
What is THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol)?

The primary cannabinoid responsible for the “high” associated with marijuana use is THC. When you consume THC, it binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain, changes the release of neurotransmitters, and leads to a range of effects, including altered reality, mood, and understanding.
THC can also be used to treat health problems. For example, it can relieve pain, stop inflammation, and stop nausea and vomiting. It has been studied as a treatment for many conditions. Here we can mention chronic pain, multiple sclerosis, and nausea and vomiting caused by chemotherapy.
But THC can also have bad effects, especially when it is taken in large amounts or for a long time. These can include impaired memory and cognitive function, anxiety, paranoia, and addiction. Additionally, the legal status of THC varies depending on where you live. It is classified as an illegal substance in many countries.
What is THCV (Tetrahydrocannabivarin)?
THCV is a cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant, along with other cannabinoids like THC and CBD. It is structurally similar to THC but has different effects on the body.
Tetrahydrocannabivarin is a psychoactive compound, meaning it can produce a “high” when consumed. However, the effects of THCV are often described as being more energising and stimulating than THC. THCV has been studied for its potential as an appetite suppressant. Because it appears to reduce feelings of hunger and may be effective in treating obesity.
Also, THCV could be used to treat diseases like diabetes. Because it seems to make insulin work better and keep blood sugar levels stable. Some studies have also suggested that THCV may have anticonvulsant effects, making it a potential treatment for conditions like epilepsy.
What is CBG (Cannabigerol)?
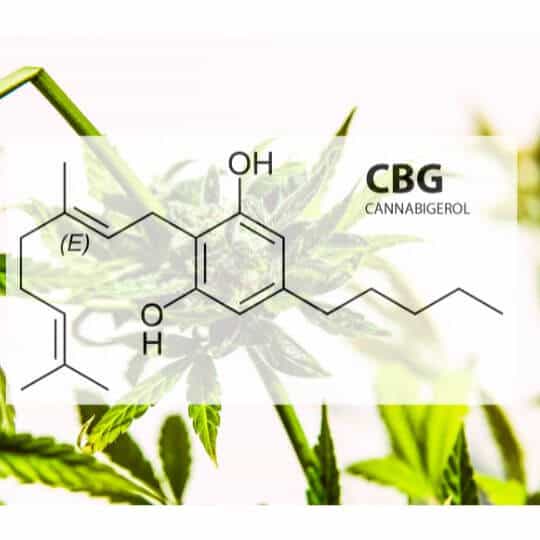
CBG is a cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant. It is a cannabinoid that isn’t as important as THC and CBD because it is usually found in lower amounts.
Cannabigerol is non-psychoactive. However, it appears to have some medicinal effects. CBG has been studied for its potential as an anti-inflammatory help. Additionally, CBG can kill some bacteria, especially on the skin. This makes it a potential treatment for conditions like MRSA.
Some studies have also suggested that CBG could be used to treat glaucoma. It seems to lower the pressure inside the eye. CBG may also have neuroprotective effects, which means it may help protect against Huntington’s.
More from our blog about CBG:
What are Endocannabinoids?
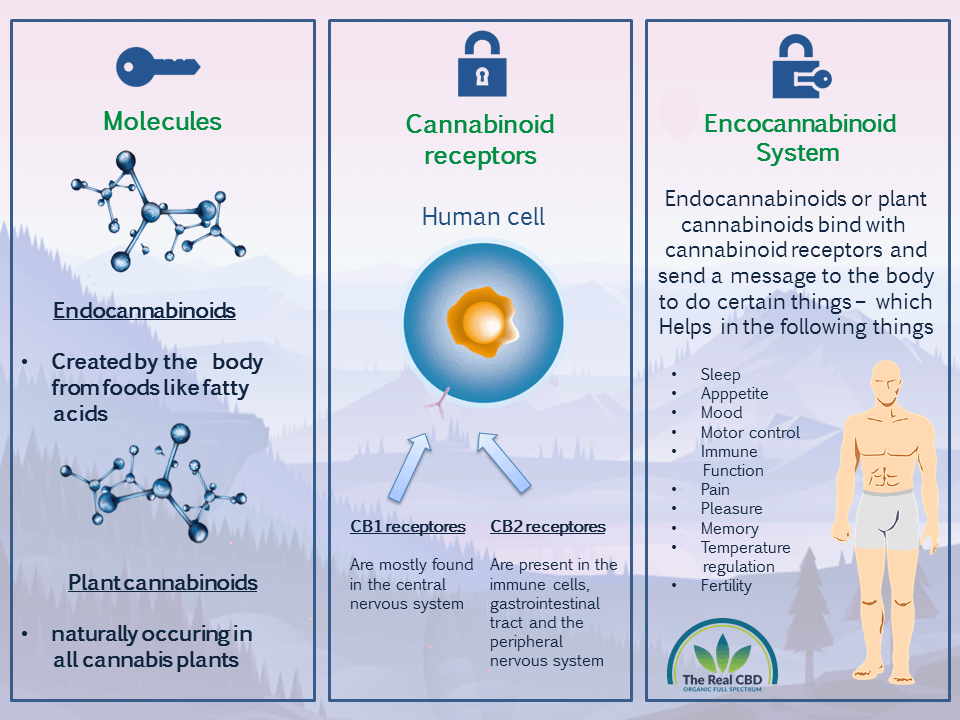
Endocannabinoids are substances that the body makes on its own. They have the same structure as the cannabinoids that come from the cannabis plant.
Researchers have found that anandamide (AEA) and 2-AG are the two main endocannabinoids. The body produces these endocannabinoids on demand in response to different stimuli, and enzymes quickly break them down.
Endocannabinoids play a complicated and not fully understood role in the body. But scientists think that they help control a number of body functions. How much pain we feel, how hungry we are, and how well our immune system works. Endocannabinoids may help heal conditions like chronic pain and inflammation,
.
What is the endocannabinoid system?
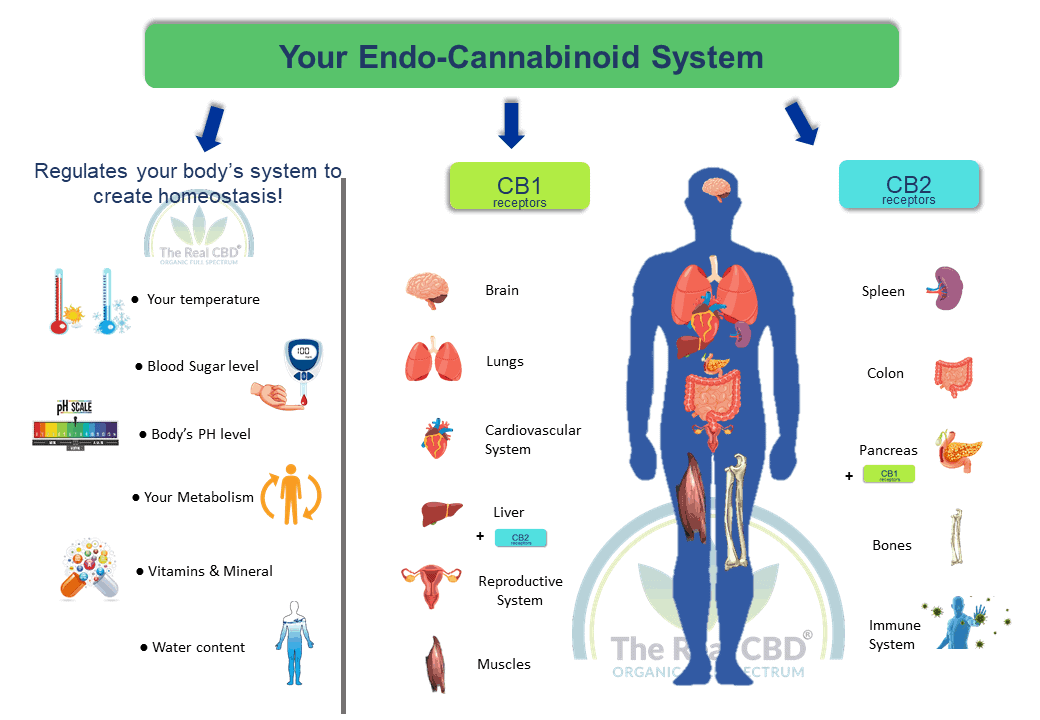
The endocannabinoid system is a complicated way for cells to talk to each other. It helps control a number of bodily functions, such as how we feel pain, how hungry we are, and how well our immune systems work.
The main parts of the ECS are endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes. Endocannabinoids are chemicals that the body makes on its own and that work with cannabinoid receptors.
Receptors are proteins that are on the outside of cells and get signals from endocannabinoids and other molecules that send signals. Endocannabinoids are broken down and get rid of from the body by enzymes.
CB1 and CB2 are the two main types of cannabinoid receptors that are found all over the body. Most CB2 receptors are in immune cells and tissues outside of the brain and central nervous system. Most CB1 receptors are in the brain and central nervous system.
Cannabinoids
FAQ – Cannabinoids

Cannabinoids are chemical compounds found in the Cannabis sativa plant. They interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system to produce various effects.
Cannabinoids interact with receptors in the endocannabinoid system, primarily CB1 and CB2 receptors, influencing processes such as pain, mood, and appetite.
The most well-known cannabinoids are THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol). THC is known for its psychoactive effects, while CBD is non-psychoactive and valued for its therapeutic benefits.
The most well-known cannabinoids are THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol). THC is known for its psychoactive effects, while CBD is non-psychoactive and valued for its therapeutic benefits.
Some cannabinoids can have side effects, such as dry mouth, dizziness, and changes in appetite. THC, in particular, can cause psychoactive effects and impaired coordination. It’s important to use cannabinoids responsibly and consult with a healthcare provider.