CBD with vitamin D can optimize your health!
Estimated reading time: 8 minutes
Introduction
They call it the sunshine vitamin. CBD with vitamin D can optimize your health in a whole new way. It is a combination of 2 of the most beneficial oils for our Endocannabinoid system. But what is vitamin D? and what is it good for? Here we will be discussing all the vitamin D benefits and how important it is for a long list of body functions. Did you know that vitamin D is actually a hormone and not a vitamin? Get all the ins and outs of one of the most potent and important supplements there are…. And most of us do not have enough!!!
1. What is vitamin D?

Vitamin D is a hormone the kidneys produce that controls blood calcium concentration and impacts the immune system. It is also known as calcitriol, ergocalciferol, calcidiol, and cholecalciferol. Of those, calcidiol is the form doctors most commonly focus on when measuring vitamin D levels in the blood.
The body makes vitamin D in a chemical reaction that occurs when sunlight hits the skin. This reaction produces cholecalciferol, and the liver converts it to calcidiol. The kidneys then convert the substance to calcitriol, which is the active form of the hormone in the body.
Vitamin D has its effects by binding to a protein (called the vitamin D receptor). This receptor is present in nearly every cell and affects many different body processes.
2. What is vitamin D good for?

Vitamin D has several important functions. Perhaps the most important 2 functions are regulating the absorption of calcium and phosphorus and facilitating normal immune system function. Getting a sufficient amount of vitamin D is important for normal growth and development of bones and teeth, as well as improved resistance against certain diseases.
If your body doesn't get enough vitamin D, you're at risk of developing bone abnormalities such as soft bones (osteomalacia) or fragile bones (osteoporosis).
How do we get vitamin D?
There are several ways of getting vitamin D:
- Spend more time in sunlight with exposed skin and no sunscreen
- Eat fatty fish and seafood
- Eat mushrooms
- Include the yolk when you consume eggs
- Choose vitamin D fortified foods
- Take a supplement
- Use lamps with UV-B light
3. What happens if vitamin D is low?

Symptoms of bone pain and muscle weakness can mean you have a vitamin D deficiency. However, for many people, the symptoms are subtle. Yet, even without symptoms. Low blood levels of the vitamin have been associated with the following:
- Increased risk of death from cardiovascular disease
- Cognitive impairment in older adults
- Severe asthma in children
- Cancer
Research suggests that vitamin D could play a role in the prevention and treatment of a number of different conditions, including type1 and type 2 diabetes, hypertension, glucose intolerance, and multiple sclerosis.
Causes of vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency can occur for a number of reasons: You don't consume the recommended levels of the vitamin over time. This is likely if you are a vegan because most of the natural sources of vitamin D are animal-based.
If your exposure to sunlight is limited. Because the body makes vitamin D when your skin is exposed to sunlight, you may be at risk of deficiency if you are home bound, live in northern latitudes or wear long robes or head coverings for religious reasons.
Being dark-skinned can also put you in a risk. The pigment melanin reduces the skin's ability to make vitamin D in response to sunlight exposure. Some studies show that older adults with darker skin are at high risk of vitamin D deficiency.
4. Vitamin D's other benefits!

Other than the above-mentioned reasons for keeping your vitamin D levels up we can add the following benefits to the list.
- Fights disease
- Helps depression
- Can boost weight loss
- Vitamin D can strengthen your muscles
- Strengthen oral health
- Help prevent type 1 and type 2 diabetes
- May help reduce the risk of certain cancers
- High blood pressure management
- Can help prevent respiratory infections
- It can help prevent cognitive decline
5. Benefits of CBD

CBD is good for your health in many ways.
One of the best-known benefits of CBD is that it can help relieve pain. CBD works by interacting with receptors in the brain and immune system to reduce pain and inflammation. Whether you have arthritis, chronic pain, or sore muscles, CBD can help you feel better without the side effects that come with standard painkillers.
Anxiety and Getting Rid of Stress
In the fast-paced world of today, worry and stress are common problems for many people. CBD has shown promise in helping people feel less anxious and more relaxed. CBD may help people with anxiety conditions like generalised anxiety, social anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) feel better by interacting with mood-regulating receptors in the brain.
Better quality of sleep
Lack of sleep can have a big effect on your general health and ability to think. CBD has been shown to help people sleep better by fixing problems like nervousness, chronic pain, and insomnia. CBD may help you get a good night's sleep by making you feel more relaxed and less pain, so you can wake up feeling refreshed and re-energized.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Many health problems, like arthritis, autoimmune diseases, and even acne, are linked to inflammation. The anti-inflammatory properties of CBD can help reduce inflammation all over the body, which can help relieve pain and support general health. CBD is a natural option to traditional anti-inflammatory drugs because it stops inflammation at its source.
Effects on the brain
CBD seems to protect nerve cells, which is a good sign that it could help keep the brain healthy. Research shows that CBD may help protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's by lowering inflammation, oxidative stress, and promoting neuroplasticity. Even though more research needs to be done, these results give hope for possible therapeutic uses in the future.
6. CBD with vitamin D can optimize health via the Endocannabinoid system
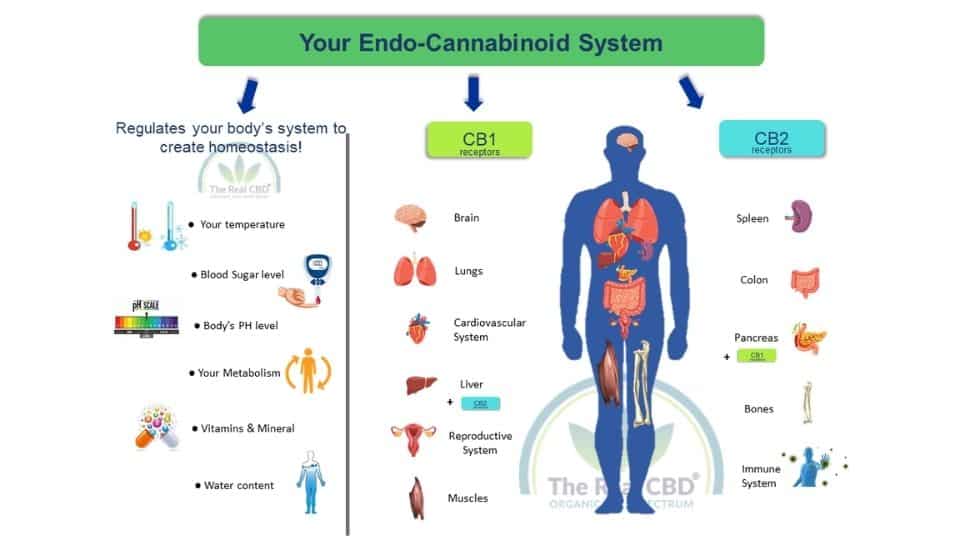
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) maintains the crucial homeostasis of many body functions and has an effect on the way our bodies regulate important body systems. This being things like stress response, sleep, and inflammation around your body. Since the ECS works with so many different body systems, there are many ways that the ECS can be thrown out of whack. Like vitamin D deficiency.
Studies have shown, there is a strong connection between the prevalence of anxiety in specific population groups, and vitamin D deficiency. In other words, this research has shown us that lower levels of vitamin D can negatively affect cellular signalling and neural activity in the brain – causing a stress response. This means, if you're not getting a lot of sunlight, or vitamin D through other means like wholefoods or supplementation, then your ECS might very well be thrown out of whack, and you might be feeling extra anxious or depressed because of it.
Vitamin D
So, what can you do? The obvious answer is to get outside more and start looking for vitamin D in your supplements and your food. If you find a CBD with vitamin D, even better. The CBD allows for the prolonged usage of stored-up endocannabinoids and can help protect your vitamin D levels!
That's one powerful dynamic duo!
More from our blog
7. Can you get too much vitamin D?

Vitamin D toxicity, also called hypervitaminosis D, is a rare but potentially serious condition that occurs when you have excessive amounts of vitamin D in your body.
Vitamin D toxicity is usually caused by large doses of vitamin D supplements — not by diet or sun exposure. That's because your body regulates the amount of vitamin D produced by sun exposure, and even fortified foods don't contain large amounts of vitamin D.
The main consequence of vitamin D toxicity is a build-up of calcium in your blood (hypercalcemia), which can cause nausea and vomiting, weakness, and frequent urination.
How much is too much?
Taking 60,000 international units (IU) a day of vitamin D for several months has been shown to cause toxicity. This level is many times higher than the U.K. Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for most adults of 600-800 IU of vitamin D a day.
8. The Real CBD products with vitamin D
-
Product on sale
 15% CBD oil with Vitamin D3Original price was: €85.00.€75.50Current price is: €75.50.
15% CBD oil with Vitamin D3Original price was: €85.00.€75.50Current price is: €75.50. -
Product on sale
 5% CBD oil with Vitamin D3Original price was: €29.00.€24.00Current price is: €24.00.
5% CBD oil with Vitamin D3Original price was: €29.00.€24.00Current price is: €24.00.

I am a certified expert in Medicinal Cannabis. We are all about giving correct and trustworthy information. We know how important it is to learn about CBD and cannabis, which is why we want to be your go-to source for trustworthy information. We help you improve your health by using our knowledge and experience as a starting point.












Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!